Mary Wants to Send a Message to Sam So That Only Sam Can Read It
What is disproportionate cryptography?
Asymmetric cryptography, also known as public-key cryptography, is a procedure that uses a pair of related keys -- i public key and one private key -- to encrypt and decrypt a message and protect it from unauthorized admission or use.
A public key is a cryptographic central that can be used by any person to encrypt a message then that information technology can only be decrypted by the intended recipient with their private central. A private fundamental -- also known as a surreptitious fundamental -- is shared only with key'south initiator.
When someone wants to send an encrypted message, they tin pull the intended recipient's public key from a public directory and use it to encrypt the message before sending it. The recipient of the bulletin can so decrypt the message using their related private key.
If the sender encrypts the message using their individual key, the bulletin tin can exist decrypted simply using that sender'southward public key, thus authenticating the sender. These encryption and decryption processes happen automatically; users exercise not need to physically lock and unlock the bulletin.
Many protocols rely on disproportionate cryptography, including the ship layer security (TLS) and secure sockets layer (SSL) protocols, which make HTTPS possible.
The encryption procedure is also used in software programs that need to establish a secure connection over an insecure network, such every bit browsers over the net, or that need to validate a digital signature.
Increased data security is the primary benefit of asymmetric cryptography. It is the most secure encryption process because users are never required to reveal or share their individual keys, thus decreasing the chances of a cybercriminal discovering a user's individual cardinal during transmission.
How does asymmetric cryptography work?
Asymmetric encryption uses a mathematically related pair of keys for encryption and decryption: a public cardinal and a private primal. If the public key is used for encryption, and then the related private key is used for decryption. If the private key is used for encryption, and so the related public key is used for decryption.
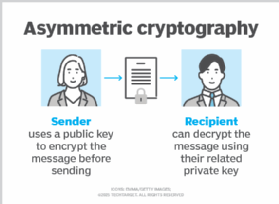
The two participants in the asymmetric encryption workflow are the sender and the receiver. Each has its own pair of public and private keys. Commencement, the sender obtains the receiver's public key. Side by side, the plaintext bulletin is encrypted by the sender using the receiver's public key. This creates ciphertext. The ciphertext is sent to the receiver, who decrypts it with their individual cardinal, returning it to legible plaintext.
Because of the one-way nature of the encryption part, i sender is unable to read the messages of some other sender, even though each has the public key of the receiver.
Uses of disproportionate cryptography
Disproportionate cryptography is typically used to authenticate data using digital signatures. A digital signature is a mathematical technique used to validate the authenticity and integrity of a bulletin, software or digital document. It is the digital equivalent of a handwritten signature or stamped seal.
Based on asymmetric cryptography, digital signatures tin can provide assurances of evidence to the origin, identity and status of an electronic certificate, transaction or message, as well every bit acknowledge informed consent by the signer.
Asymmetric cryptography can also be applied to systems in which many users may demand to encrypt and decrypt messages, including:
- Encrypted e-mail. A public key can exist used to encrypt a message and a private key can be used to decrypt it.
- SSL/TLS. Establishing encrypted links betwixt websites and browsers also makes utilize of asymmetric encryption.
- Cryptocurrencies . Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies rely on asymmetric cryptography. Users have public keys that everyone can run across and private keys that are kept secret. Bitcoin uses a cryptographic algorithm to ensure only legitimate owners can spend the funds.
In the example of the Bitcoin ledger, each unspent transaction output (UTXO) is typically associated with a public key. For example, if user X, who has an UTXO associated with his public primal, wants to transport the money to user Y, user 10 uses his private cardinal to sign a transaction that spends the UTXO and creates a new UTXO that's associated with user Y's public fundamental.
What are the benefits and disadvantages of asymmetric cryptography?
The benefits of asymmetric cryptography include:
- The central distribution trouble is eliminated because there's no need for exchanging keys.
- Security is increased since the private keys don't e'er have to be transmitted or revealed to anyone.
- The use of digital signatures is enabled and so that a recipient tin verify that a bulletin comes from a particular sender.
- It allows for nonrepudiation and then the sender can't deny sending a message.
Disadvantages of asymmetric cryptography include:
- It's a dull process compared to symmetric cryptography. Therefore, it'southward not appropriate for decrypting bulk messages.
- If an private loses his private key, he can't decrypt the messages he receives.
- Because public keys aren't authenticated, no one can ensure a public key belongs to the person specified. Consequently, users must verify that their public keys vest to them.
- If a malicious actor identifies a person's private central, the assaulter tin can read that individual's letters.
What's the departure between asymmetric vs. symmetric cryptography?
The principal deviation between asymmetric versus symmetric cryptography is that asymmetric encryption algorithms make employ of two unlike merely related keys. Ane key encrypts data and another fundamental decrypts it. Symmetric encryption uses the aforementioned key to perform both encryption and decryption functions.
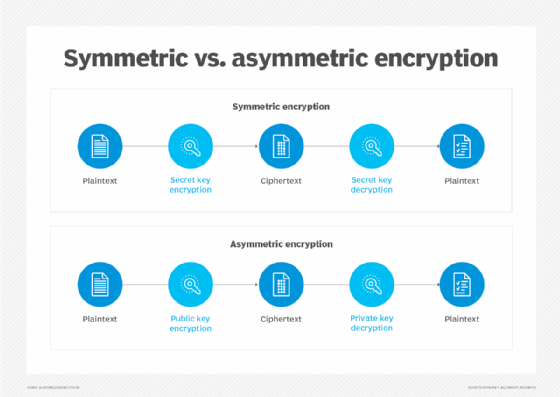
Some other difference between disproportionate and symmetric encryption is the length of the keys. In symmetric cryptography, the length of the keys -- which is randomly selected -- are typically set at 128 bits or 256 bits, depending on the level of security needed.
In disproportionate encryption, in that location must exist a mathematical relationship between the public and private keys. Since malicious actors can potentially exploit this pattern to cleft the encryption, asymmetric keys demand to exist longer to offering the aforementioned level of security. The difference in the length of the keys is then pronounced that a 2048-chip asymmetric key and a 128-chip symmetric key provide nigh an equivalent level of security.
Asymmetric encryption is notably slower than symmetric encryption, which has a faster execution speed.
What are examples of asymmetric cryptography?
The RSA algorithm -- the near widely used disproportionate algorithm -- is embedded in the SSL/TLS, which is used to provide secure communications over a reckoner network. RSA derives its security from the computational difficulty of factoring large integers that are the production of ii big prime number numbers.
Multiplying 2 big primes is easy, but the difficulty of determining the original numbers from the product -- factoring -- forms the basis of public-key cryptography security. The fourth dimension it takes to factor the product of two sufficiently large primes is beyond the capabilities of about attackers.
RSA keys are typically 1024 or 2048 $.25 long, merely experts believe 1024-bit keys volition be broken soon, which is why government and industry are moving to a minimum key length of 2048-bits.
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) is gaining favor with many security experts equally an alternative to RSA. ECC is a public-primal encryption technique based on elliptic curve theory. Information technology can create faster, smaller and more efficient cryptographic keys through the properties of the elliptic curve equation.
To suspension ECC, an attacker must compute an elliptic curve discrete logarithm, which is significantly more than difficult problem than factoring. Equally a result, ECC key sizes can exist significantly smaller than those required by RSA while still delivering equivalent security with lower calculating power and battery resource usage.
What's the history of disproportionate cryptography?
Whitfield Diffie and Martin Hellman, researchers at Stanford University, first publicly proposed disproportionate encryption in their 1977 paper, "New Directions in Cryptography."
The concept was independently and covertly proposed past James Ellis several years earlier, while he was working for the Government Communications Headquarters (GCHQ), the British intelligence and security organization. The asymmetric algorithm as outlined in the Diffie-Hellman newspaper uses numbers raised to specific powers to produce decryption keys. Diffie and Hellman initially teamed upward in 1974 to solve the problem of central distribution.
The RSA algorithm, which was based on the piece of work of Diffie, was named after its three inventors -- Ronald Rivest, Adi Shamir and Leonard Adleman. They invented the RSA algorithm in 1977 and published it in Communications of the ACM in 1978.
Mary Wants to Send a Message to Sam So That Only Sam Can Read It
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/definition/asymmetric-cryptography